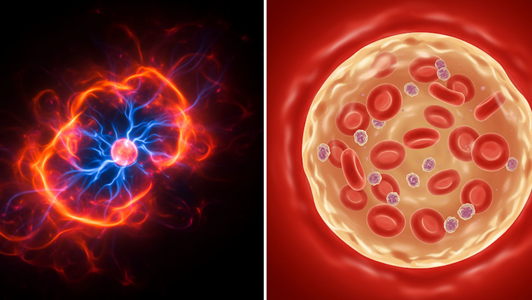
Plasma, as a physical state of matter, exists in the surroundings of the Sun, inside nuclear fusion reactors, and around hypersonic missiles. The term “plasma” is also used in biology, where “blood plasma” refers to the liquid component of blood, and “cell plasma” or “cytoplasm” refers to the liquid substance that surrounds the components of a cell. Despite the similarity in names, biological plasma differs fundamentally from physical plasma.
What is Physical Plasma?
Physical plasma is a state of matter, often known as the fourth state, similar to a gas, but with a key difference: it contains a large number of electrically charged particles. Instead of neutral atoms or molecules, plasma consists of free electrons and ions (atoms or molecules that have lost or gained electrons).
This ionization process usually occurs when a gas is exposed to very high temperatures or strong electromagnetic fields. These conditions provide enough energy to strip electrons from their atoms. When atoms gain enough energy, their electrons can overcome the attractive force of the nucleus and become free, leaving behind positively charged ions and a sea of negatively charged electrons. This mixture of charged particles is what characterizes physical plasma.
One of the most prominent properties of plasma is its ability to conduct electricity and the presence of magnetic fields that arise within it, due to the presence of charged particles. This allows it to conduct electricity more efficiently than neutral gases and also allows external magnetic fields to influence it.
Blood Plasma and Cytoplasm: Different from the Fourth State of Matter
The term “plasma” is used in biology to describe components of living organisms, but it differs from the “fourth state of matter” known as physical plasma. Biological plasma, such as blood plasma and cytoplasm (cell plasma), are essentially liquids or semi-liquids within the body and do not share the fundamental properties of physical plasma.
Blood Plasma:
Blood plasma is the yellowish, watery liquid part of blood. It is a complex mixture that carries many vital substances throughout the body, including water, proteins, salts, hormones, and antibodies that fight infections. The main function of blood plasma is transportation, delivering nutrients and oxygen to cells and removing waste products. It is essentially liquid and not like the high-energy ionized gas that physicists call the fourth state of matter or plasma.
Cytoplasm (Cell Plasma):
Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the inside of a cell. It surrounds the internal structures of the cell, such as mitochondria (the cell’s powerhouses) and the nucleus (which contains the cell’s genetic material). Cytoplasm plays a key role in transporting materials within the cell and provides an aqueous environment where various salts and proteins work together to maintain proper cell function. It is not physical plasma; rather, it is an aqueous environment that supports the complex processes that occur within cells.
Why is Plasma Named This Way?
The term “blood plasma” was first used in 1839 by the Czech medical scientist Johannes Purkinje to describe the liquid component of blood. The word plasma itself is derived from the ancient Greek word “πλάσμα” (plásma), which means “that which is formed or molded.”
Then, the American physicist Irving Langmuir coined the term “plasma” to describe the fourth state of matter (ionized gas) in 1928, comparing it to blood plasma, and noted that the way blood plasma carries red and white corpuscles reminded him of how ionized gas carries electrons and ions. This suggests that the prior medical use of the term plasma directly influenced its adoption in physics.
As for the term “cytoplasm,” it was introduced in 1863 by Rudolf von Kölliker to refer to the substance within the cell, outside the nucleus, and combines “cyto-” (cell) with “-plasm,” which has the same Greek root as the word “plasma.”
Conclusion
Although physical plasma, blood plasma, and cytoplasm share the name, they are completely different concepts. Physical plasma is a state of matter containing free electrons and ions, and it is considered the fourth state of matter. It can be said that it is a gas but charged. While blood plasma and cytoplasm are liquid biological components and are not considered the fourth state of matter.