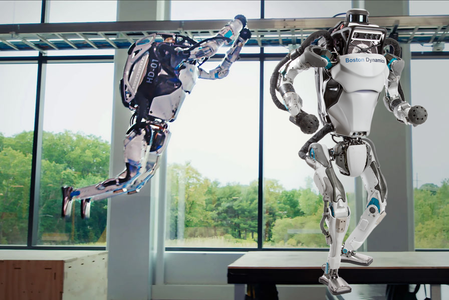
The robot Atlas was unveiled to the public in 2013, developed by Boston Dynamics, which releases successive videos about its latest achievements, showing its impressive agility and balance capabilities. It is able to walk, run, jump,flip, overcome obstacles, perform complex movements and carry heavy objects.
It has a robust body design and powerful hydraulic actuators that make it capable of handling heavy objects.
It was initially funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to create a robot capable of performing difficult tasks such as search and rescue. In 2021 Hyundai Motor Group completed its acquisition of Boston Dynamics.
How does Atlas move in the environment?
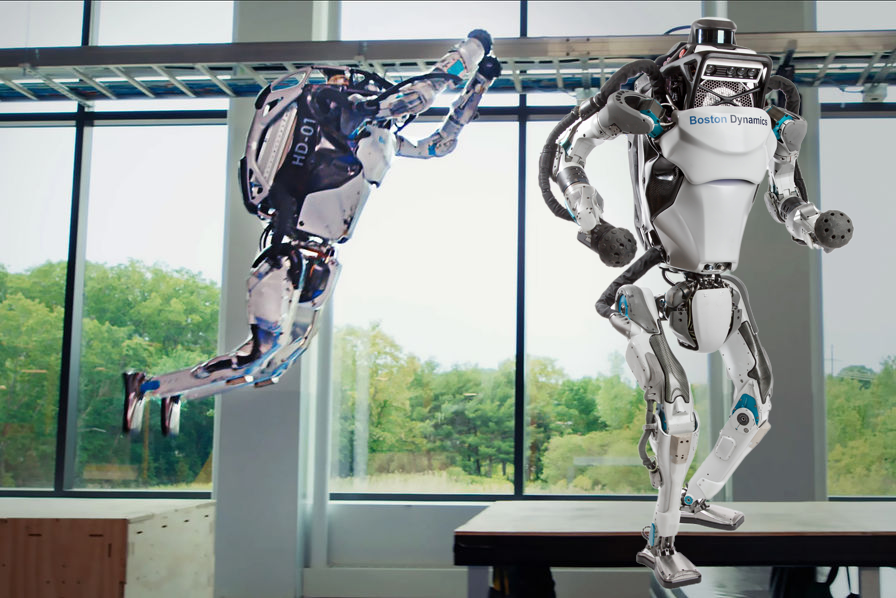
Atlas collects data using many sensors, cameras, and lidar to build a 3D model of the surrounding environment. It represents the objects around and their boundaries (orange lines), and then the planning algorithm suggests its next moves ( green footsteps in the image below). The robot then independently executes the required calculations to navigate towards its intended place.
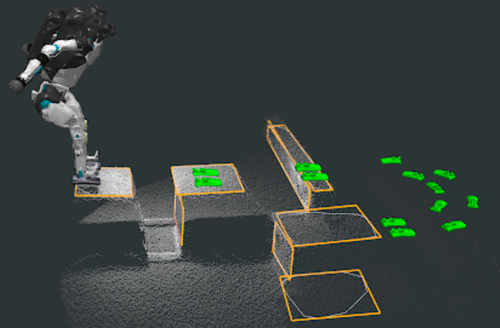
At first, the robot's movements were planned out by hand, with engineers deciding its path step-by-step. Thus, Atlas relies on pre-programmed instructions for movement, rather than independent decision-making.
But After executing many pre-defined trajectories, Atlas got a template library, and it became possible to move independently, thanks to a special controller that chooses the optimal next step from the template library based on its surroundings and its internal state. For example, if it finds a cylindrical barrier in front of it, the controller will recognize the need to hop over the obstacle and execute a jump seamlessly.
Why is it not used to perform useful work?
So far, Atlas is still a research platform and has not been used for commercial purposes; But in the last published video, it appeared assisting with work in an automobile factory - like the Tesla Optimus robot or the Figure 01 robot which recently began training at the BMW factory - suggests it could move beyond research labs and into practical use.
What is missing from Atlas?
Autonomy; In order for a robot to be useful, it needs to have some kind of autonomy and intelligence to carry out specific tasks. Beyond executing pre-programmed motions, robots need flexible decision-making to perform specific tasks and achieve different goals. Atlas's current approach doesn't offer this adaptability, limiting its real-world usefulness.
Atlas represents a cutting-edge platform for future robot development, but its real-world impact will depend on its ability to leverage AI for successful task execution.