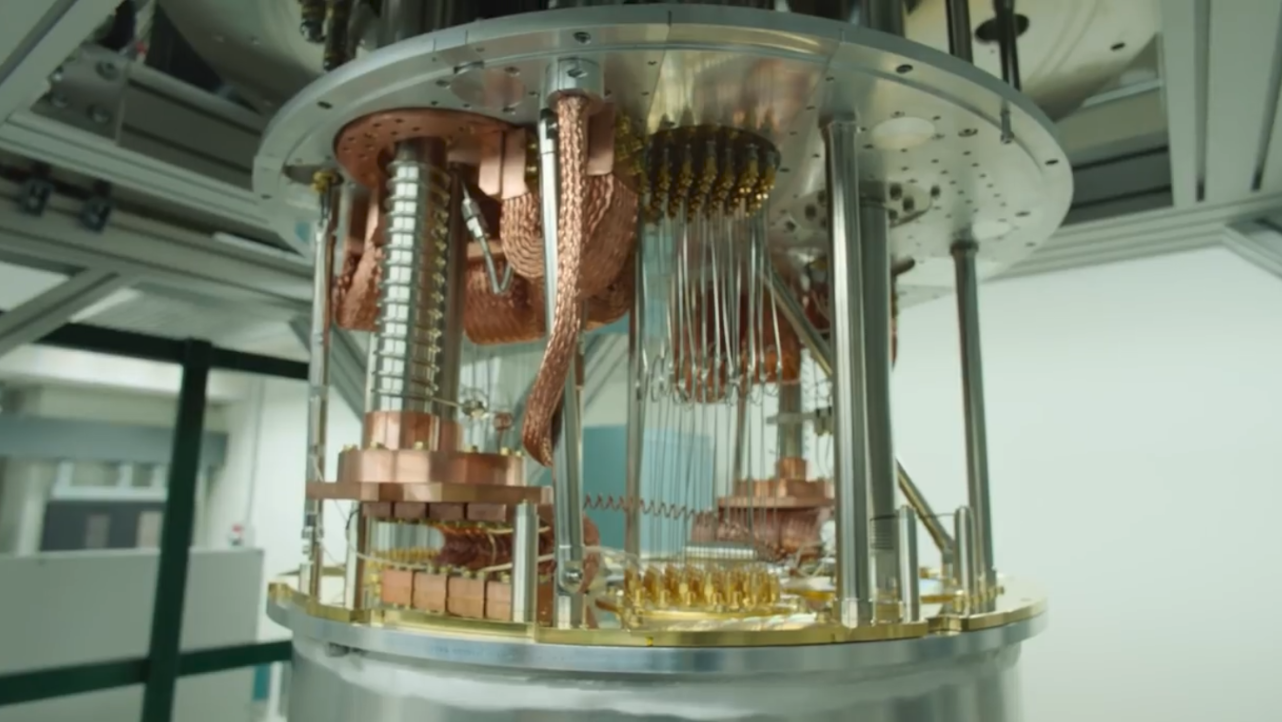
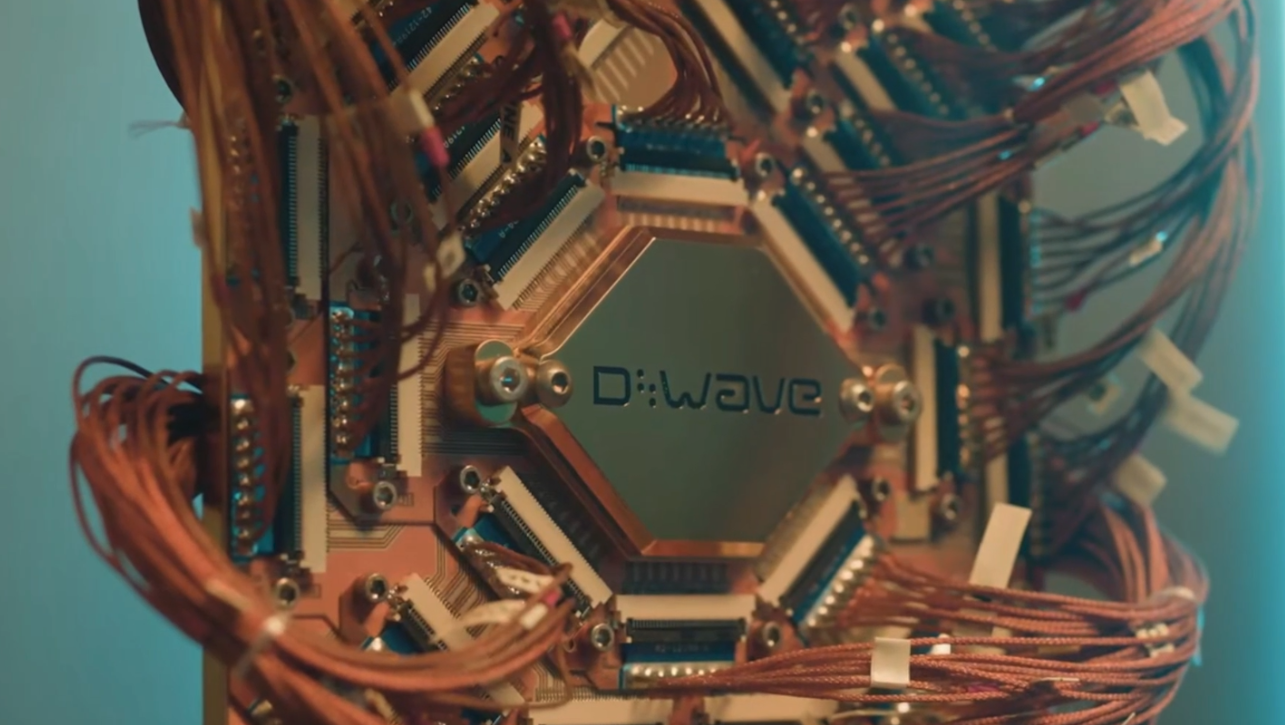
Quantum computing enables the processing of massive amounts of data at extremely high speeds. Unlike conventional computers, quantum computers do not use bits that exist in only two states. Instead, they use qubits, or quantum bits, which can exist in multiple states simultaneously, significantly increasing computational power.
Interacting with qubits and transferring information to and from them is one of the most prominent challenges in quantum computers. Each qubit is connected to a wire to transmit signals, and these wires hinder the increase in the number of qubits and cause the problem of thermal noise.
A qubit needs to remain at a very low temperature close to absolute zero (-273 degrees). However, the passage of electrical signals in the wires generates heat that causes thermal noise, so large amounts of energy must be consumed to cool the entire system.
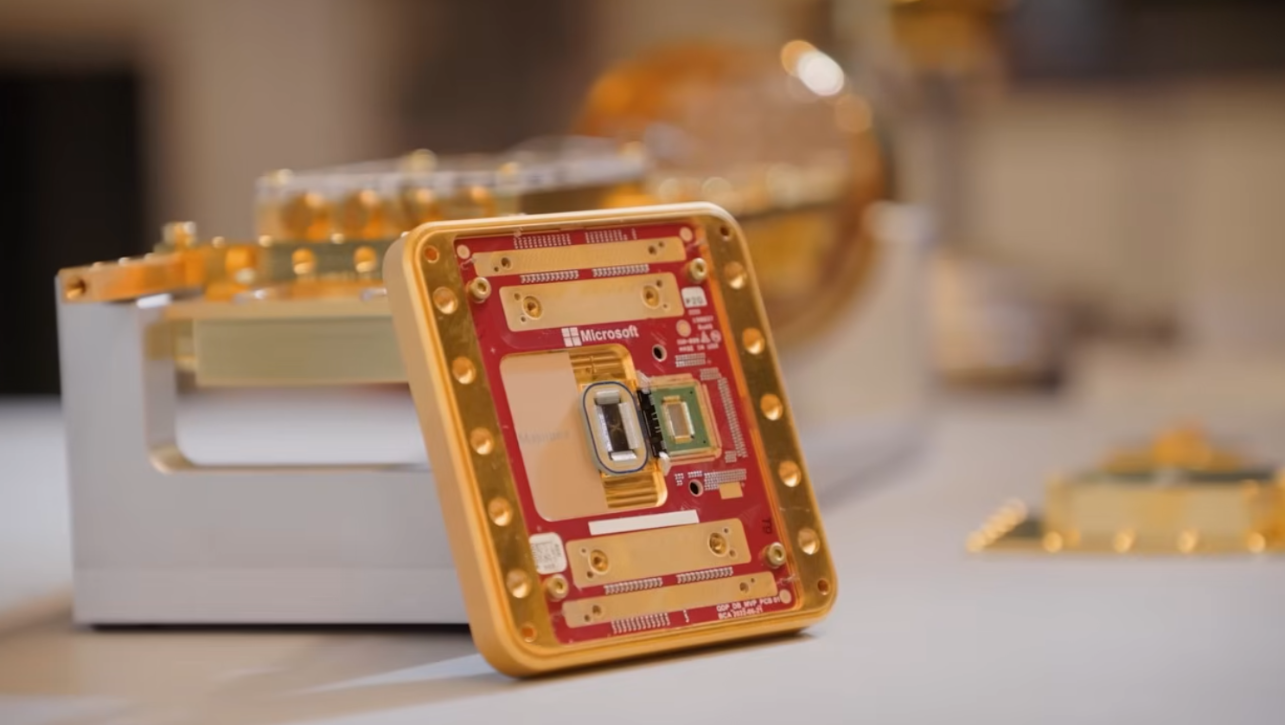
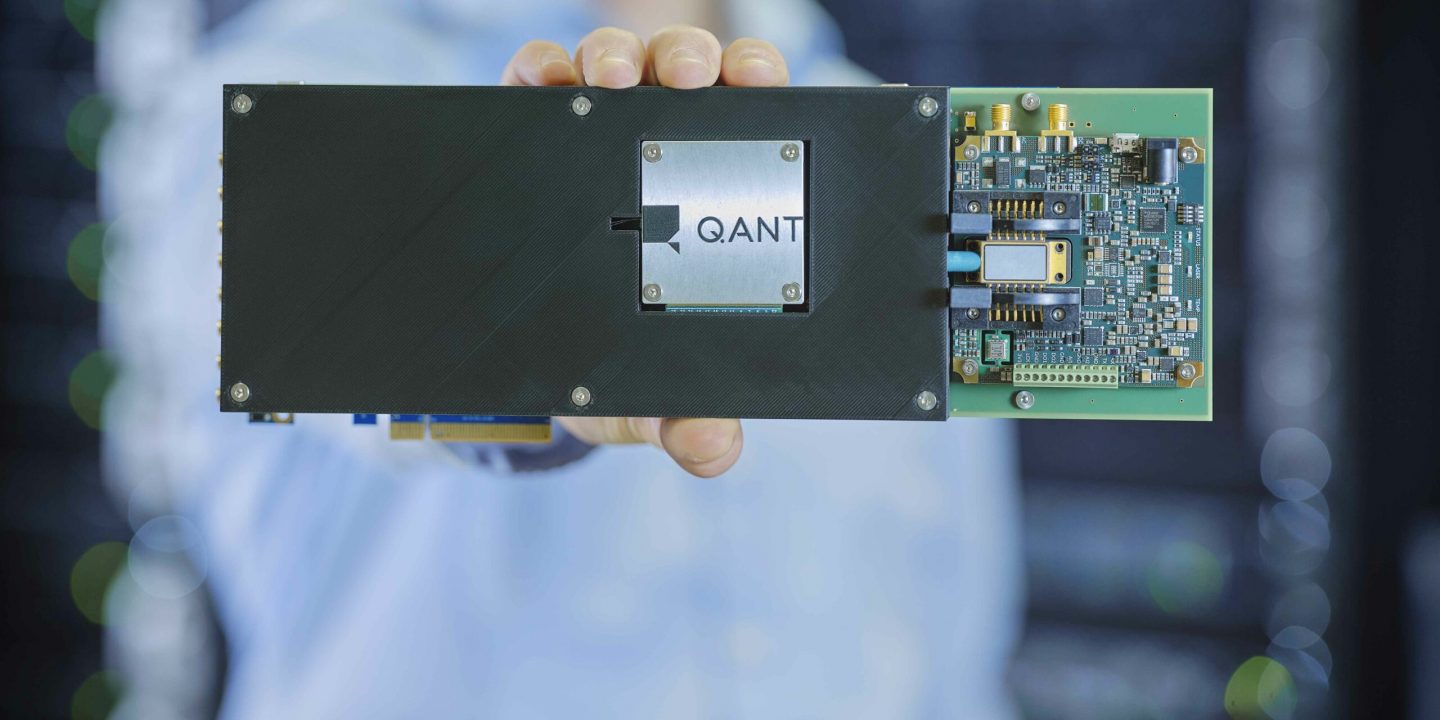
To address these challenges, researchers at the Institute of Science and Technology in Austria(ISTA) have developed a new technology that relies on optical fibers instead of electrical wires, which greatly reduces the need for cooling. The new technology uses an electro-optical converter to read qubits using microwaves. The microwaves are then converted into light pulses that travel through optical fibers, which use less energy and generate less heat. Conversely, the optical signals are converted into microwave signals to be sent to the qubits.
The use of optical fibers has many advantages. They are faster in transmitting information, produce less heat, and therefore require less cooling. They also have a higher bandwidth, which makes the structure simpler. Instead of connecting each qubit to a wire, the same optical cable can be used to transmit information from more than one qubit, which simplifies the structure and manufacturing process.
Thanks to this innovation, the structure of the quantum computer has become simpler and requires less energy to cool, which paves the way for the manufacture of reliable and practical quantum computers at a lower cost and the possibility of expanding the capabilities of its processor by adding qubits without major complications in the structure.