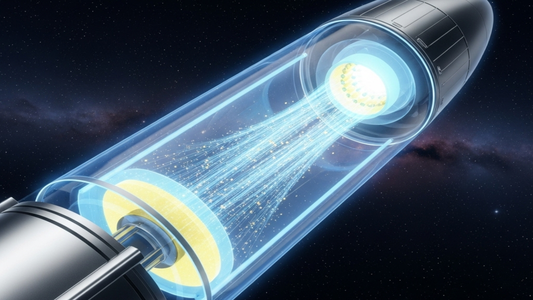
NASA has announced the TFINER project, an initiative aimed at developing a nuclear space propulsion system that utilizes thin-film layers of radioisotopes, eliminating the need for chemical reactions or moving parts. The goal is to provide spacecraft with an efficient and sustainable propulsion system, enabling long-duration space travel and maneuverability without requiring continuous fuel resupply.
This propulsion system relies on thin layers of active radioisotopes, such as Thorium-228, Actinium-227, and Curium-242, which naturally emit high-energy alpha particles. These emissions are carefully directed to collide with a substrate and produce a reaction force that propels the spacecraft forward.
Unlike traditional propulsion systems, which expel mass like hot gases, TFINER does not rely on moving parts, combustion, or excessive heat generation. However, while it offers continuous thrust, it cannot generate the high force needed for rocket launches or escaping Earth’s gravity. Instead, it is ideal for spacecraft operating in deep space, where small yet consistent thrust can accumulate over time. Over months or years, this gradual acceleration allows spacecraft to reach velocity changes of up to 100 km/s — or even 150 km/s in advanced configurations — according to NASA. This speed is more than five times faster than NASA’s Voyager 1, which travels at 17 km/s.
As of now, no experimental prototype of the TFINER propulsion system has been built. The project requires advancements in radioisotope production and further refinement of its design to maximize energy utilization. If successful, TFINER could revolutionize space propulsion, expanding the possibilities of interstellar exploration. It has the potential to radically change spacecraft design, reducing reliance on massive fuel reserves and complex propulsion systems, making interstellar travel more efficient and sustainable.