Researchers at the Russian company Rosatom have unveiled a plasma electric rocket engine capable of propelling spacecraft to Mars within a period of one to two months, significantly reducing space travel time.
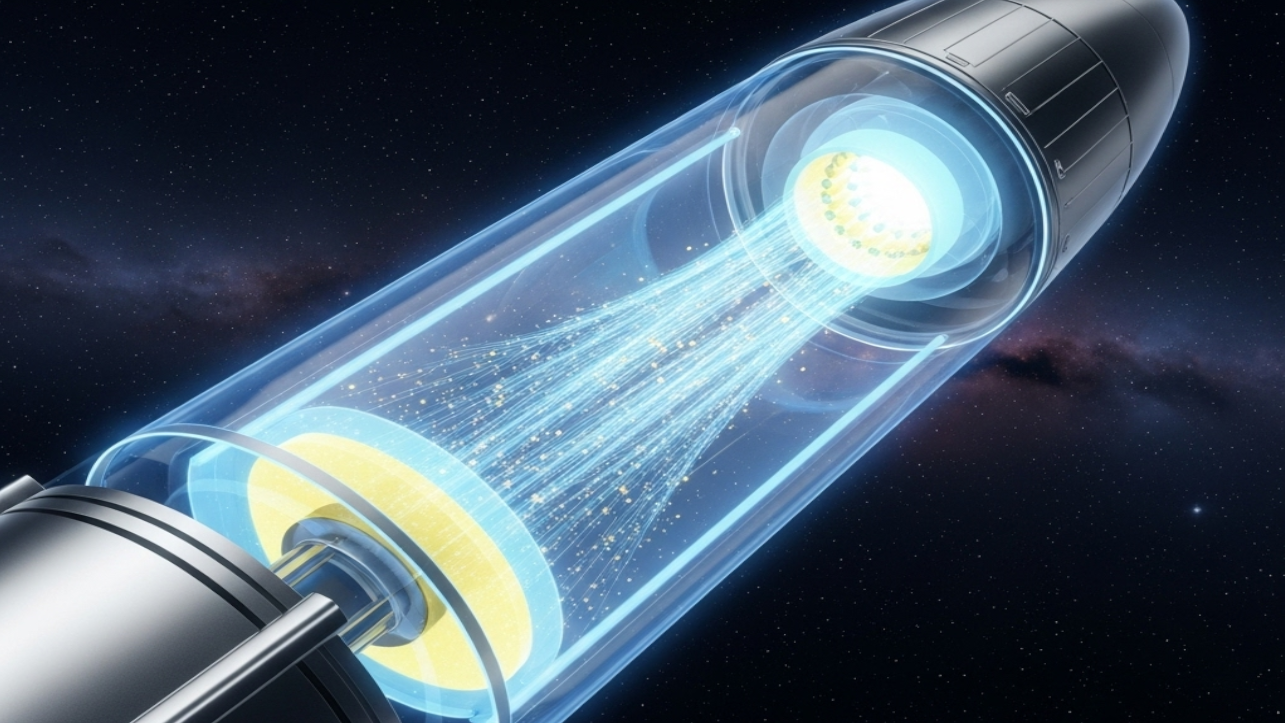
The plasma engine is a type of electric engine, where hydrogen gas is first converted into plasma by applying high voltage across the engine’s electrodes. This process strips electrons from the hydrogen atoms, creating plasma composed of free charges: negative electrons and positive ions.
The high-voltage electric current also generates an electric field that accelerates the charged particles, causing them to create a magnetic field. The interaction between the electric and magnetic fields propels the charged particles out of the engine at high speeds, generating thrust that propels the spacecraft forward.
The engine can accelerate charged particles to a speed of 100 km/s, while the maximum speed of matter flow in traditional power units is about 4.5 km/s. This makes it highly efficient and capable of achieving much higher speeds compared to chemical rocket engines that rely on fuel combustion.
A laboratory prototype of the engine has already been developed at the Troitsk Institute affiliated with Rosatom. Additionally, a test stand has been built, consisting of a chamber with a diameter of 4 meters and a length of 14 meters, designed to simulate space conditions. This prototype will undergo extensive ground testing to optimize its operational modes and pave the way for the creation of a flight model, expected to be ready by 2030.
The engine operates at a power of 300 kilowatts and generates a thrust of 6 newtons, the highest among similar projects so far. It has already been operated continuously for 2,400 hours, which is theoretically sufficient to transport a spacecraft to Mars.